




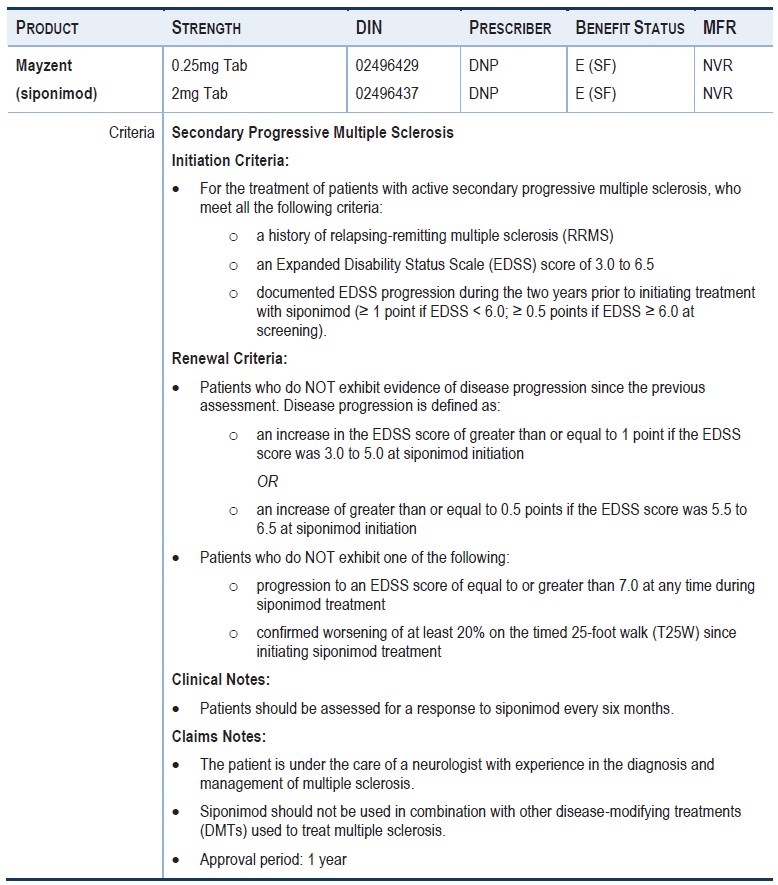



For thetreatment of people with secondary progressive multiple sclerosis.
Uponinitiation of treatment, the person should:
Have activedisease characterized by at least one of the following:
-A clinical relapse within the past two years.
-A new lesion in T2 within thelast year
-An increase in the volume of a T2 lesion inthe last year
-A gadolinium-enhanced lesion on magnetic resonanceimaging (MRI) within the last year
and have an EDSS score of less than 7
Approvals are given at a maximum dose of 2mg per day
The maximumduration of each authorization is 12 months
When requesting continued treatment, the physician must confirm that the EDSS score is below 7.
Treatment has to be initiated in all patients with a starter pack that lasts for 5 days . The dose titration starts with 0.25 mg once daily on day 1 and day 2, followed by once daily doses of 0.5 mg on day 3, 0.75 mg on day 4, and 1.25 mg on day 5 , to reach the maintenance dose of 2 mg* MAYZENT starting on day 6.
The recommended maintenance dose is 1 mg daily for patients with CYP2C9 *2*3 or *1*3 genotype
During titration (when using the starter pack), the recommended daily dose should be taken once daily in the morning with or without food. If a titration dose is missed on one day during the first 6 days of treatment (Day 1 to Day 6, from titration to the first day of the maintenance dose), treatment needs to be re-initiated with Day 1 of the titration regimen, using a new starter pack.
Initiation of treatment with MAYZENT causes a transient decrease in heart rate and atrioventricular conduction delays. Prescribers should:
Obtain an electrocardiogram (ECG) for all patients to determine whether pre-existing conduction abnormalities are present (see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS, Cardiovascular – Treatment Initiation Recommendations and Bradyarrhythmia and Atrioventricular Conduction Delays).
Determine whether patients are taking concomitant medications that reduce heart rate or atrioventricular conduction (see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS, Cardiovascular – Bradyarrhythmia and Atrioventricular Conduction Delays; and DRUG INTERACTIONS).
For patients with sinus bradycardia (heart rate (HR) <55 bpm), first or second-degree [Mobitz type I] atrioventricular block (AV block), or a history of myocardial infarction or heart failure, prepare to administer the first dose of MAYZENT in a clinical setting where they can be monitored for signs and symptoms of bradycardia, with hourly pulse and blood pressure measurements for at least 6 hours, and where symptomatic bradycardia can be managed (see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS, Cardiovascular – Treatment Initiation Recommendations).
For patients with certain other pre-existing cardiac conditions, seek an evaluation from a cardiologist prior to initiating treatment, to assess suitability of treatment and to determine the most appropriate strategy for monitoring cardiac effects (see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS, Cardiovascular – Treatment Initiation Recommendations).