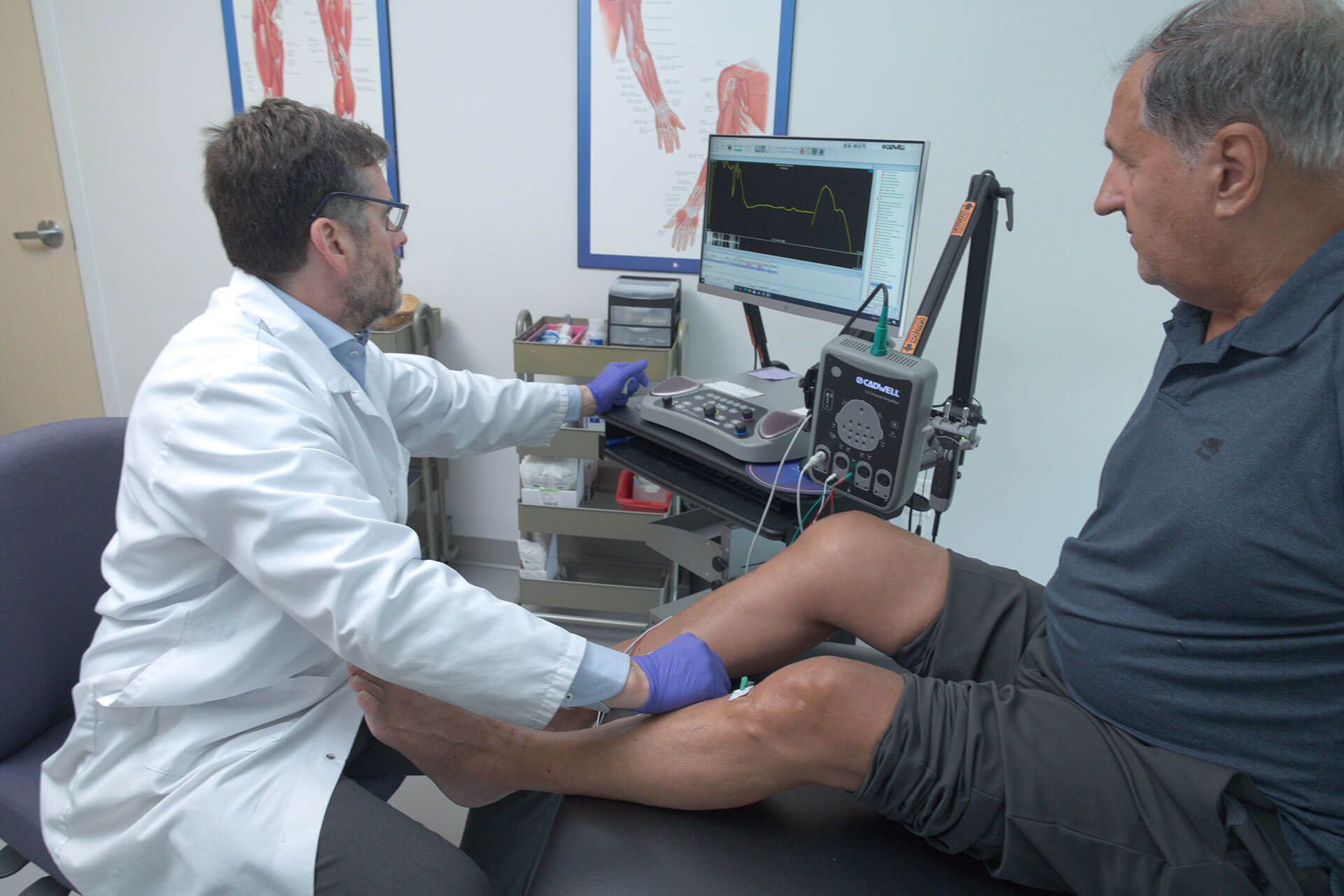
ALS is characterized by progressive weakness, muscle atrophy, and stiffness in the limbs or bulbar muscles, which control speech and swallowing. In some individuals, it may also be accompanied by cognitive changes and alterations in personality.
ALS is a uniformly fatal condition, with most patients surviving an average of 3 to 5 years after diagnosis. The underlying cause and disease mechanisms remain poorly understood.
While current medications such as Riluzole and Edaravone (Radicava) may modestly extend survival, they do not halt disease progression or improve quality of life. Supportive therapies, physiotherapy, occupational therapy, nocturnal ventilation assist, nutritional assistance via feeding tube etc., remain the mainstay of treatment.
Research is ongoing for both symptomatic treatment and disease modifying therapies.
Non-invasive neuro modulation using repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) has been shown to alleviate ALS symptoms, including weakness and spasticity.
rTMS is however still considered an experimental treatment and is not yet covered by public health plans (RAMQ/OHIP)
2022: Himalaya study (Phase II)