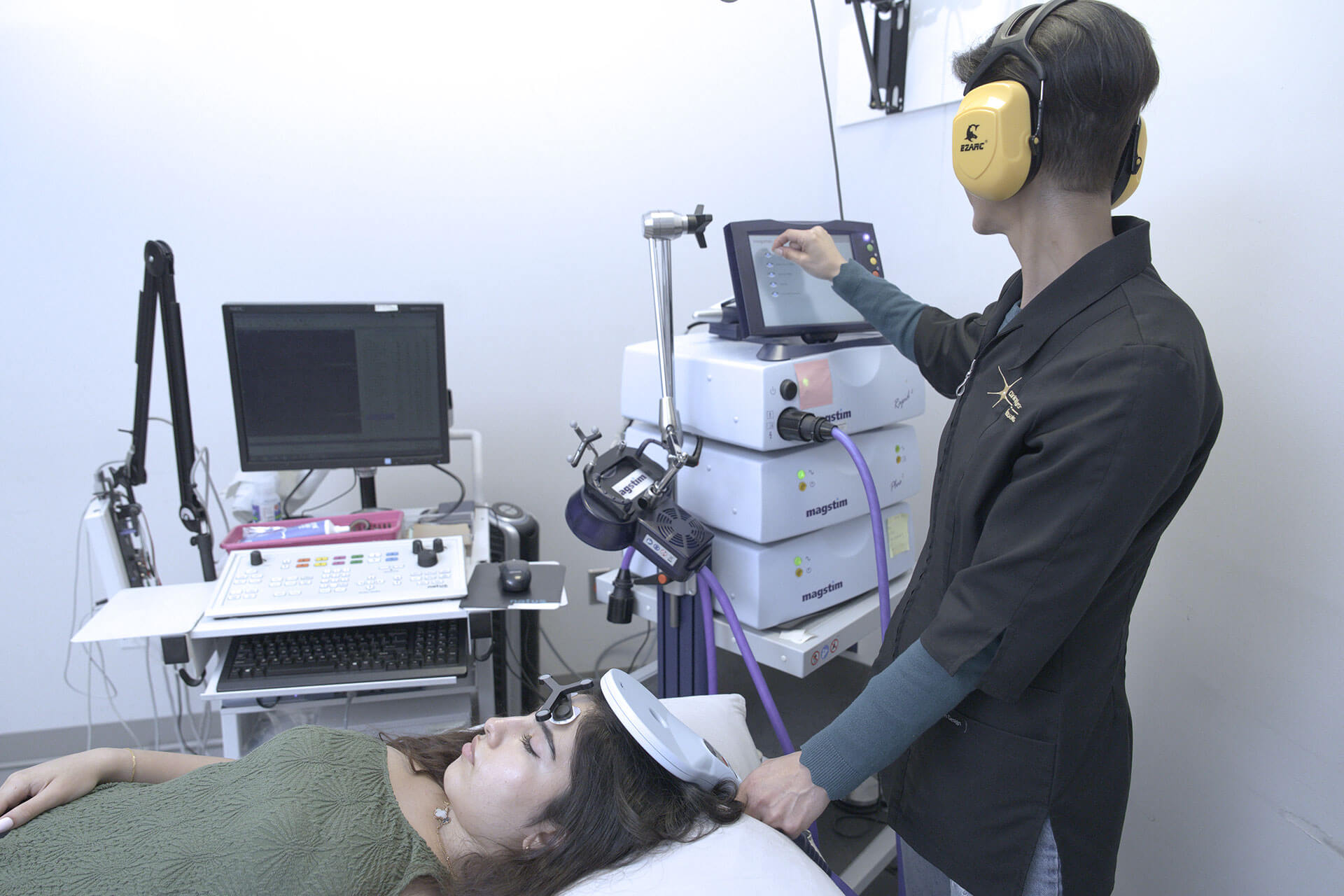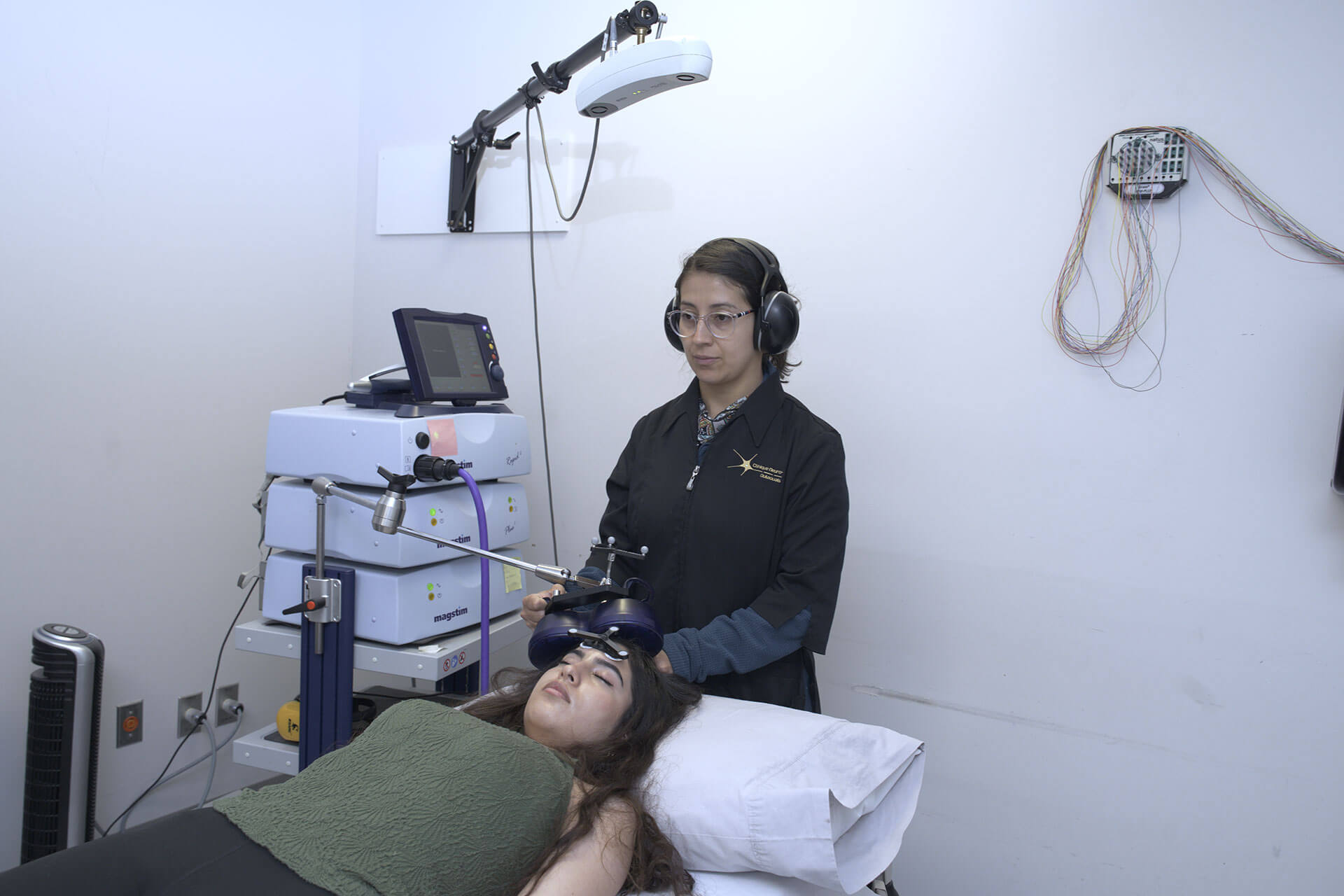
rTMS is a safe and non-invasive procedure that uses an electromagnet to generate small, focused, repetitive currents in the superficial layers of the brain. When these currents are delivered repeatedly over time, they help modulate the brain’s functional and structural connectivity, promoting neuroplasticity—the brain’s natural ability to reorganize and adapt.
In essence, rTMS leverages our inherent neuroplasticity to help the brain overcome neuronal injury or disease, opening the door to promising new avenues in neurological care.
CNO is also actively conducting clinical research using rTMS for conditions such as Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM).